问题背景
在微服务的 application.properties 文件中有一个 test.container-name 配置。原始配置如下:- test.container-name=Tomcat
- @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test")
- @Component
- public class TestConfigProperty {
- private String containerName;
-
- public String getContainerName() {
- return containerName;
- }
-
- public void setContainerName(String containerName) {
- this.containerName = containerName;
- }
- }
- test.container-name=${TEST_CONTAINER_NAME}
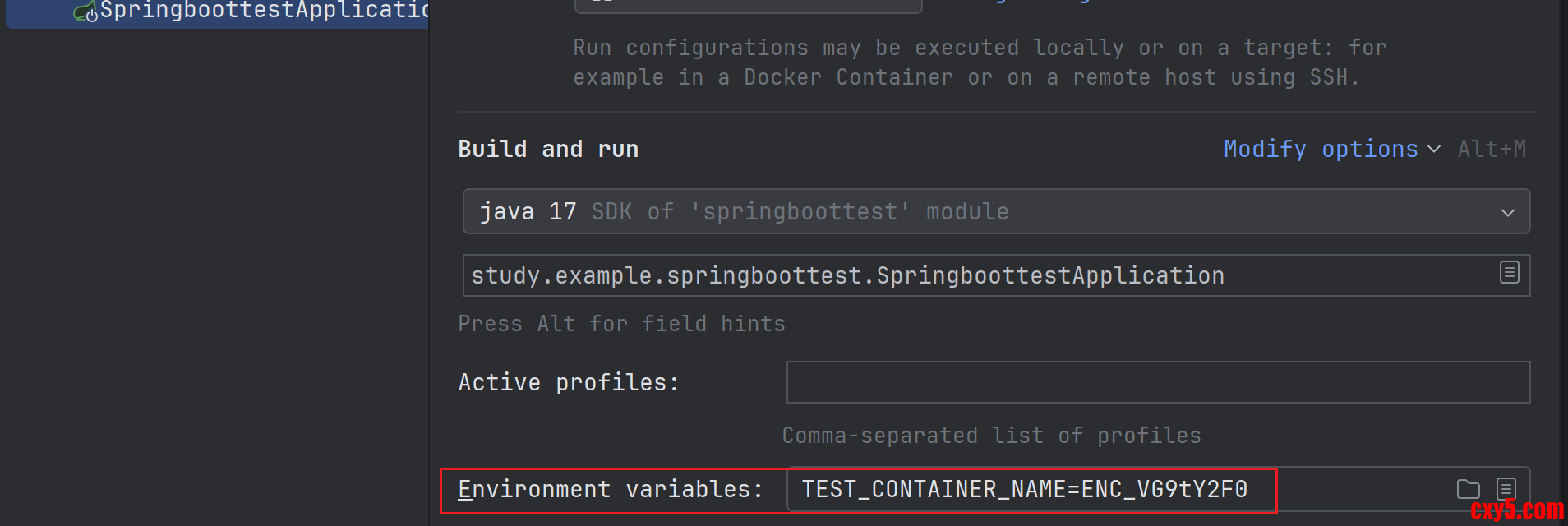
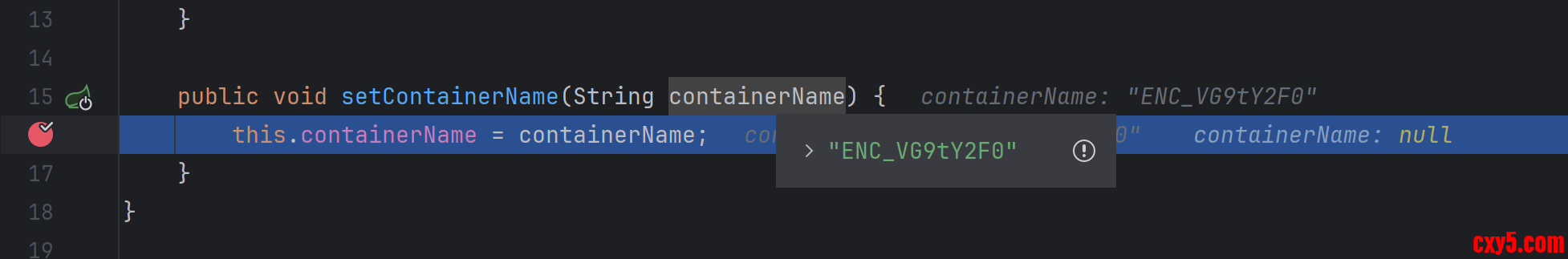
在项目中有框架提供了在微服务启动时对加密后的字符串解密的能力,实现的基本原理是提供了一个 DecryptEnvironmentPostProcessor 类扩展了 EnvironmentPostProcessor。
在它的 postProcessEnvironment() 方法中,判断环境变量配置的值是否是以 ENC_ 开头,如果是则进行解密。解密之后放到一个 MapPropertySource 里面,然后添加到所有的 PropertySource 的前面。示例代码如下:- public class DecryptEnvironmentPostProcessor implements EnvironmentPostProcessor, Ordered {
- private static final String DECRYPTED_SOURCE_NAME = "decryptedSystemEnvironment";
-
- @Override
- public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
- String systemEnvName = StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
- MapPropertySource systemEnvSource = (MapPropertySource) environment.getPropertySources().get(systemEnvName);
- Map<String, Object> decryptedMap = new HashMap<>();
- if (systemEnvSource == null) {
- return;
- }
- systemEnvSource.getSource().forEach((key, value) -> {
- if (value instanceof String strVal) {
- // 这里进行了解密
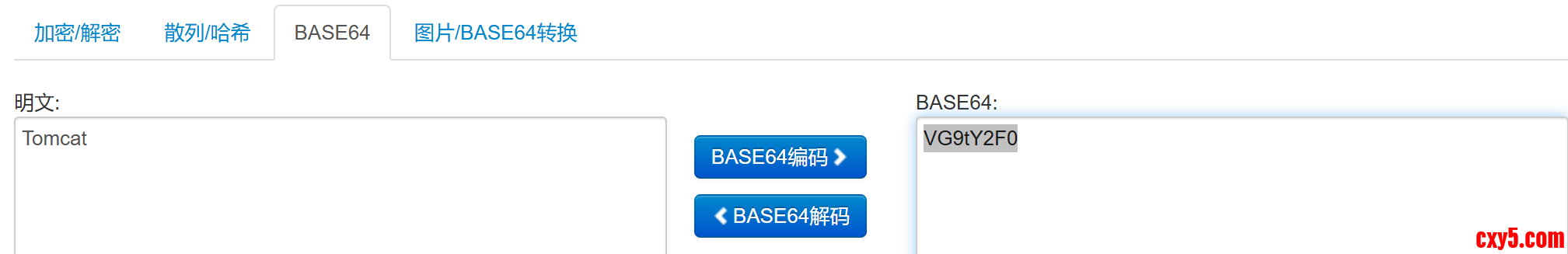
- if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(strVal) && strVal.startsWith("ENC_")) {
- String plainText = new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode(strVal.substring(4)));
- decryptedMap.put(key, plainText);
- }
- }
- });
-
- if (!decryptedMap.isEmpty()) {
- MapPropertySource decryptedSource = new MapPropertySource(DECRYPTED_SOURCE_NAME, decryptedMap);
- // 这里添加到所有的PropertySource的前面
- environment.getPropertySources().addBefore(systemEnvName, decryptedSource);
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public int getOrder() {
- return Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
- }
- }
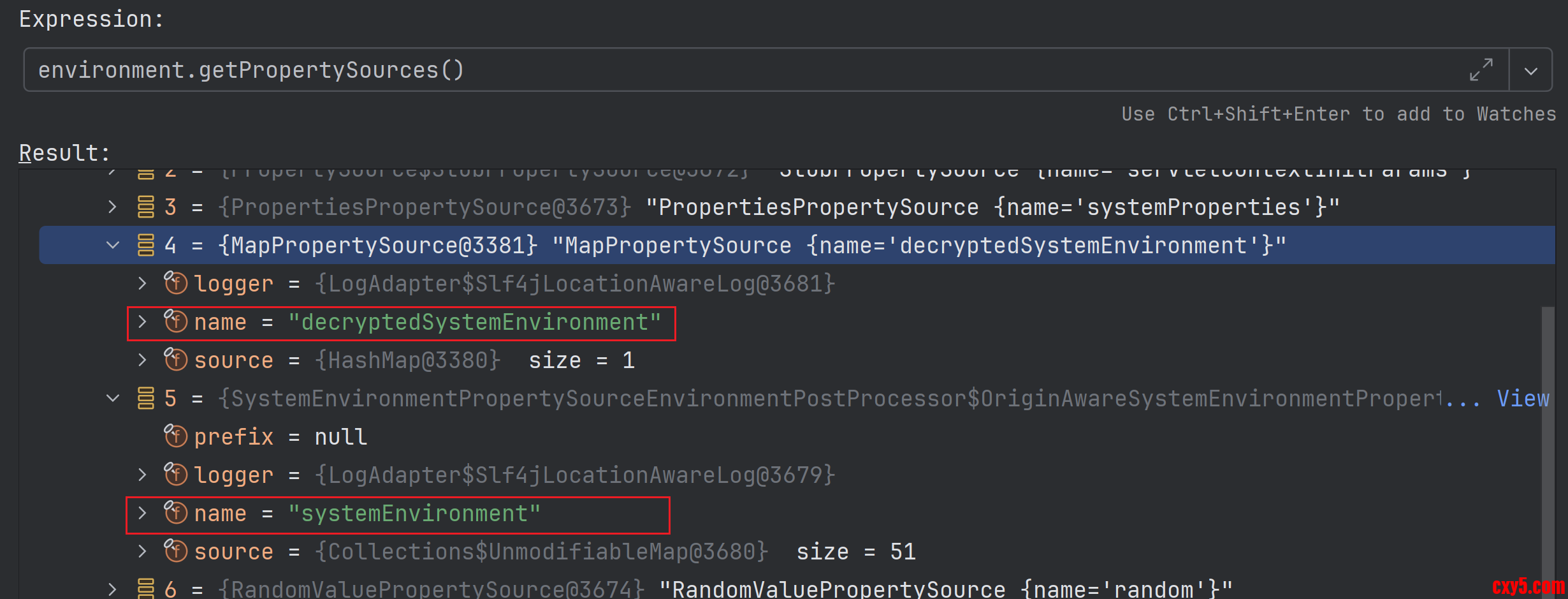
查看 Environment 的 getPropertySources() 方法的返回值中,解密之后的环境变量属性配置确实是在未解密的环境变量属性配置之前,按照直观上的理解,那应该注入的是解密之后的值才对,但是实际结果却不是这样的。如下图所示:
问题原理
之前的文章这就是宽松的适配规则!里面讲了宽松适配的原理。在 Spring 的框架体系中是在 ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor 中的 postProcessBeforeInitialization() 中实现对有 @ConfigurationProperties 注解修饰类的属性进行绑定的。
在它的内部实际上是通过调用 ConfigurationPropertiesBinder 的 bind() 来实现属性绑定的。代码如下:- public class ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor
- implements BeanPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean {
- @Override
- public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
- if (!hasBoundValueObject(beanName)) {
- bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean.get(this.applicationContext, bean, beanName));
- }
- return bean;
- }
-
- private void bind(ConfigurationPropertiesBean bean) {
- if (bean == null) {
- return;
- }
- Assert.state(bean.asBindTarget().getBindMethod() != BindMethod.VALUE_OBJECT,
- "Cannot bind @ConfigurationProperties for bean '" + bean.getName()
- + "'. Ensure that @ConstructorBinding has not been applied to regular bean");
- try {
- // 这里实际上是调用了ConfigurationPropertiesBinder的bind()方法
- this.binder.bind(bean);
- }
- catch (Exception ex) {
- throw new ConfigurationPropertiesBindException(bean, ex);
- }
- }
- }
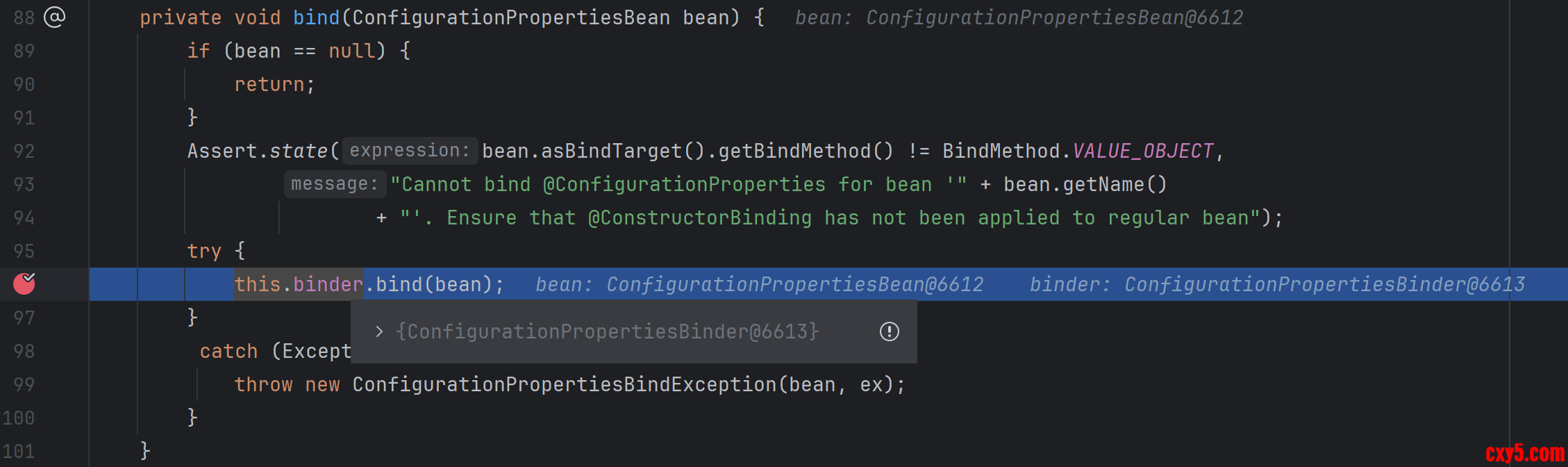
在 ConfigurationPropertiesBinder 的 bind() 方法又调用了 Binder 的 bind() 方法。如下图所示:
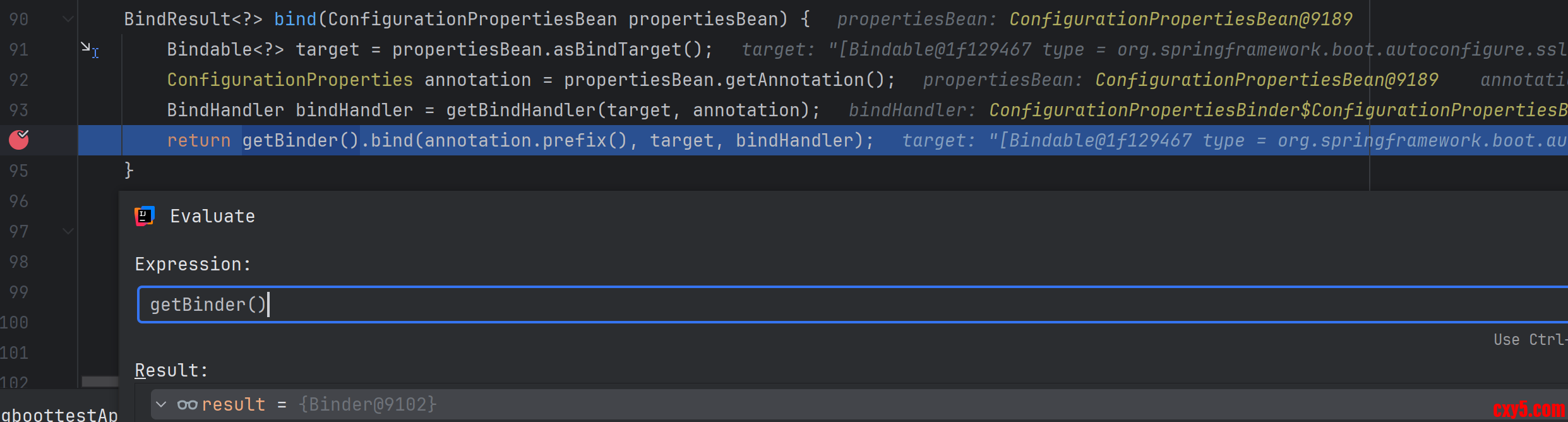
在调用 Binder 的 bind() 方法时,会把注解上配置的前缀传进去,在本案例中就是 test,并基于这个前缀创建一个 ConfigurationPropertyName 对象,然后最终调用到 bindObject() 方法。代码如下:- public class Binder {
- public <T> BindResult<T> bind(String name, Bindable<T> target, BindHandler handler) {
- // 这里基于test前缀创建了ConfigurationPropertyName对象
- return bind(ConfigurationPropertyName.of(name), target, handler);
- }
-
- private <T> T bind(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<T> target, BindHandler handler, Context context,
- boolean allowRecursiveBinding, boolean create) {
- try {
- Bindable<T> replacementTarget = handler.onStart(name, target, context);
- if (replacementTarget == null) {
- return handleBindResult(name, target, handler, context, null, create);
- }
- target = replacementTarget;
- // 调用bindObject()方法
- Object bound = bindObject(name, target, handler, context, allowRecursiveBinding);
- return handleBindResult(name, target, handler, context, bound, create);
- }
- catch (Exception ex) {
- return handleBindError(name, target, handler, context, ex);
- }
- }
- }
- public class Binder {
- private <T> Object bindObject(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<T> target, BindHandler handler,
- Context context, boolean allowRecursiveBinding) {
- ConfigurationProperty property = findProperty(name, target, context);
- if (property == null && context.depth != 0 && containsNoDescendantOf(context.getSources(), name)) {
- return null;
- }
- // 省略中间代码
-
- //调用bindDataObject()方法
- return bindDataObject(name, target, handler, context, allowRecursiveBinding);
- }
- private Object bindDataObject(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<?> target, BindHandler handler,
- Context context, boolean allowRecursiveBinding) {
- if (isUnbindableBean(name, target, context)) {
- return null;
- }
- Class<?> type = target.getType().resolve(Object.class);
- BindMethod bindMethod = target.getBindMethod();
- if (!allowRecursiveBinding && context.isBindingDataObject(type)) {
- return null;
- }
-
- // 注意这里的lambda表达式,在JavaBeanBinder的bind()方法最终又会调用到这个lambda表达式
- DataObjectPropertyBinder propertyBinder = (propertyName, propertyTarget) -> bind(name.append(propertyName),
- propertyTarget, handler, context, false, false);
-
- // 这里会调用到JavaBeanBinder的bind()方法
- return context.withDataObject(type, () -> fromDataObjectBinders(bindMethod,
- (dataObjectBinder) -> dataObjectBinder.bind(name, target, context, propertyBinder)));
- }
- }
- class JavaBeanBinder implements DataObjectBinder {
- @Override
- public <T> T bind(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<T> target, Context context,
- DataObjectPropertyBinder propertyBinder) {
- boolean hasKnownBindableProperties = target.getValue() != null && hasKnownBindableProperties(name, context);
- Bean<T> bean = Bean.get(target, hasKnownBindableProperties);
- if (bean == null) {
- return null;
- }
- BeanSupplier<T> beanSupplier = bean.getSupplier(target);
- boolean bound = bind(propertyBinder, bean, beanSupplier, context);
- return (bound ? beanSupplier.get() : null);
- }
-
- private <T> boolean bind(DataObjectPropertyBinder propertyBinder, Bean<T> bean, BeanSupplier<T> beanSupplier,
- Context context) {
- boolean bound = false;
- for (BeanProperty beanProperty : bean.getProperties().values()) { // 获取这个对象上所有的BeanProperty属性
- bound |= bind(beanSupplier, propertyBinder, beanProperty);
- context.clearConfigurationProperty();
- }
- return bound;
- }
-
- private <T> boolean bind(BeanSupplier<T> beanSupplier, DataObjectPropertyBinder propertyBinder,
- BeanProperty property) {
- String propertyName = determinePropertyName(property);
- ResolvableType type = property.getType();
- Supplier<Object> value = property.getValue(beanSupplier);
- Annotation[] annotations = property.getAnnotations();
- Object bound = propertyBinder.bindProperty(propertyName, //这个地方实际上又反调用回Binder中的lambda表达式了
- Bindable.of(type).withSuppliedValue(value).withAnnotations(annotations));
- if (bound == null) {
- return false;
- }
- if (property.isSettable()) {
- property.setValue(beanSupplier, bound);
- }
- else if (value == null || !bound.equals(value.get())) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("No setter found for property: " + property.getName());
- }
- return true;
- }
- }
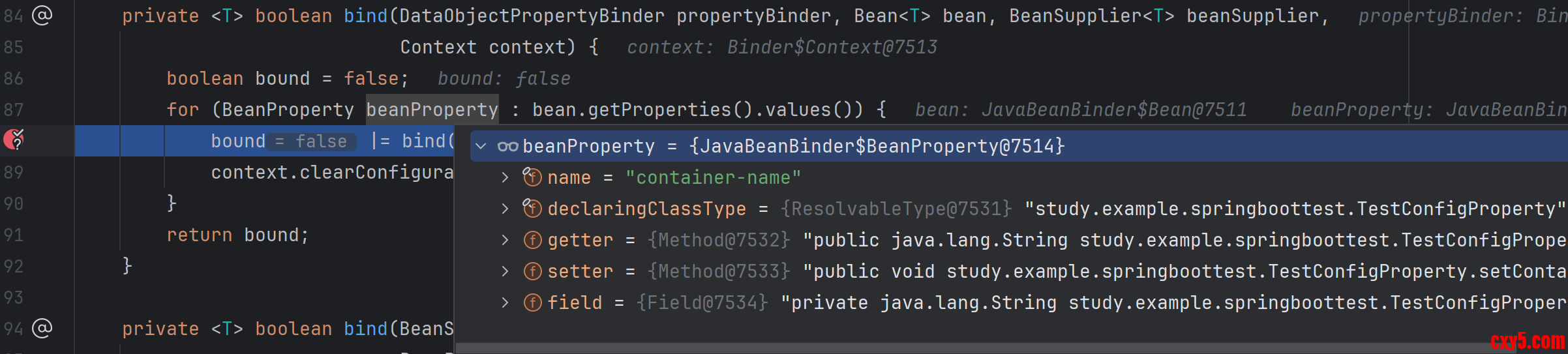
在 Binder 中 lambda 表达式会将属性拼接到已有的 ConfigurationPropertyName 前缀上,在本案例中就变成了 test.container-name。然后又递归调用 bind() 方法,然后又调用 findProperty() 方法尝试从从对应的 ConfigurationPropertySource 中获取对应的配置中查找这个属性。
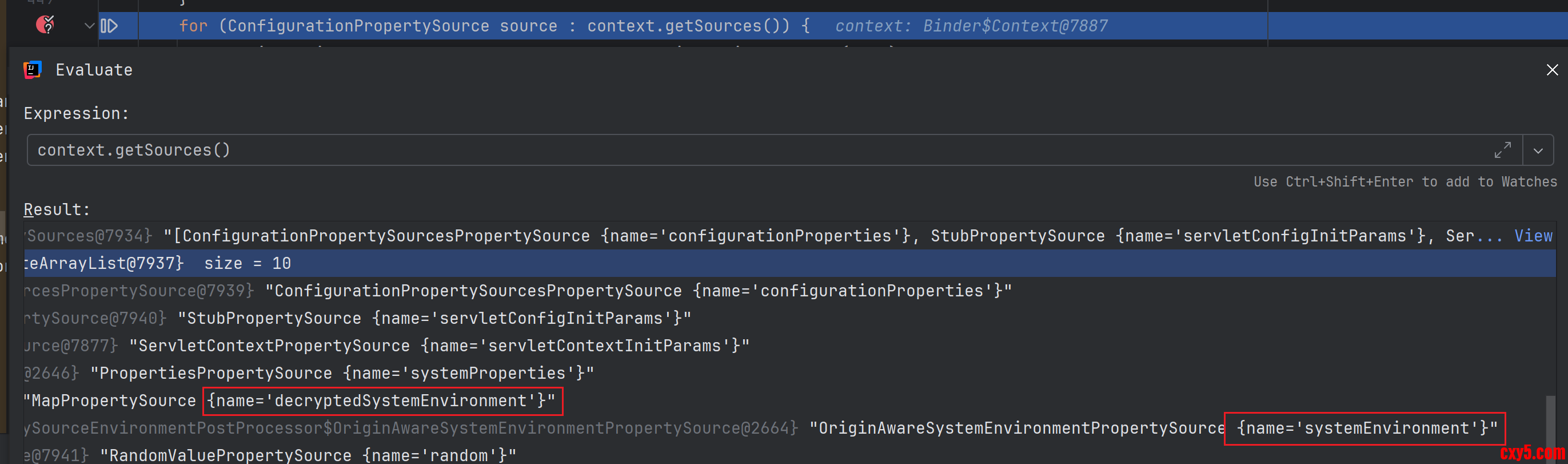
Spring 提供了 SpringIterableConfigurationPropertySource 作为 ConfigurationPropertySource 实现类, 它实际是对 PropertySource 的一个适配,内部有一个 propertySource 表示真正的配置。通过调试 contex.getSource() 方法的返回值,可以看到加密之后的 PropertySource 确实是在没有加密的前面。代码如下:- DataObjectPropertyBinder propertyBinder = (propertyName, propertyTarget) -> bind(name.append(propertyName), //这里将属性名称拼接到test前缀上
- propertyTarget, handler, context, false, false);
-
- private <T> ConfigurationProperty findProperty(ConfigurationPropertyName name, Bindable<T> target,
- Context context) {
- if (name.isEmpty() || target.hasBindRestriction(BindRestriction.NO_DIRECT_PROPERTY)) {
- return null;
- }
- for (ConfigurationPropertySource source : context.getSources()) {
- ConfigurationProperty property = source.getConfigurationProperty(name);
- if (property != null) {
- return property;
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
在 getConfigurationProperty() 方法中首先调用父类 SpringConfigurationPropertySource 的 getConfigurationProperty() 方法。在该方法中会调用 PropertyMapper 的 map() 方法对传入的 ConfigurationPropertyName 类型的 name 进行转换,然后根据转换后拿到的名称去 PropertySource 中获取对应的属性。- class SpringConfigurationPropertySource implements ConfigurationPropertySource {
- public ConfigurationProperty getConfigurationProperty(ConfigurationPropertyName name) {
- if (name == null) {
- return null;
- }
- for (PropertyMapper mapper : this.mappers) {
- try {
- for (String candidate : mapper.map(name)) { // 这里先通过PropertyMapper转换名称
- Object value = getPropertySource().getProperty(candidate); // 根据转换后的名称获取获取对应的属性
- if (value != null) {
- Origin origin = PropertySourceOrigin.get(this.propertySource, candidate);
- return ConfigurationProperty.of(this, name, value, origin);
- }
- }
- }
- catch (Exception ex) {
- // Ignore
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
- }
- class SpringConfigurationPropertySource implements ConfigurationPropertySource {
- private static final PropertyMapper[] DEFAULT_MAPPERS = { DefaultPropertyMapper.INSTANCE };
- private static final PropertyMapper[] SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_MAPPERS = { SystemEnvironmentPropertyMapper.INSTANCE,
- DefaultPropertyMapper.INSTANCE };
-
- static SpringConfigurationPropertySource from(PropertySource<?> source) {
- Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
- PropertyMapper[] mappers = getPropertyMappers(source);
- if (isFullEnumerable(source)) {
- return new SpringIterableConfigurationPropertySource((EnumerablePropertySource<?>) source, mappers);
- }
- return new SpringConfigurationPropertySource(source, mappers);
- }
-
- private static PropertyMapper[] getPropertyMappers(PropertySource<?> source) {
- // 这里判断了如果是SystemEnvironmentPropertySource则会返回SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_MAPPERS,里面包含了SystemEnvironmentPropertyMapper
- if (source instanceof SystemEnvironmentPropertySource && hasSystemEnvironmentName(source)) {
- return SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_MAPPERS;
- }
- return DEFAULT_MAPPERS;
- }
- }
- final class DefaultPropertyMapper implements PropertyMapper {
- @Override
- public List<String> map(ConfigurationPropertyName configurationPropertyName) {
- // Use a local copy in case another thread changes things
- LastMapping<ConfigurationPropertyName, List<String>> last = this.lastMappedConfigurationPropertyName;
- if (last != null && last.isFrom(configurationPropertyName)) {
- return last.getMapping();
- }
- // 这里直接返回ConfigurationPropertyName的名称
- String convertedName = configurationPropertyName.toString();
- List<String> mapping = Collections.singletonList(convertedName);
- this.lastMappedConfigurationPropertyName = new LastMapping<>(configurationPropertyName, mapping);
- return mapping;
- }
- }
- final class SystemEnvironmentPropertyMapper implements PropertyMapper {
- public static final PropertyMapper INSTANCE = new SystemEnvironmentPropertyMapper();
- @Override
- public List<String> map(ConfigurationPropertyName configurationPropertyName) {
- String name = convertName(configurationPropertyName);
- String legacyName = convertLegacyName(configurationPropertyName);
- if (name.equals(legacyName)) {
- return Collections.singletonList(name);
- }
- // 这里会返回两个格式的名称
- return Arrays.asList(name, legacyName);
- }
- private String convertName(ConfigurationPropertyName name) {
- return convertName(name, name.getNumberOfElements());
- }
- private String convertName(ConfigurationPropertyName name, int numberOfElements) {
- StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
- for (int i = 0; i < numberOfElements; i++) {
- if (!result.isEmpty()) {
- result.append('_');
- }
- result.append(name.getElement(i, Form.UNIFORM).toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
- }
- return result.toString();
- }
- private String convertLegacyName(ConfigurationPropertyName name) {
- StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
- for (int i = 0; i < name.getNumberOfElements(); i++) {
- if (!result.isEmpty()) {
- result.append('_');
- }
- result.append(convertLegacyNameElement(name.getElement(i, Form.ORIGINAL)));
- }
- return result.toString();
- }
- private Object convertLegacyNameElement(String element) {
- return element.replace('-', '_').toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
- }
- }
名称为 systemEnvironment 的 PropertySource 类型是 SystemEnvironmentPropertySource,存放的内容是 TEST_CONTAINER_NAME=ENC_VG9tY2F0。它有DefaultPropertyMapper 和 SystemEnvironmentPropertyMapper。
decryptedSystemEnvironment 在顺序上排在 systemEnvironment 前面。这个时候开始查找传入名称为 test.container-name 的 ConfigurationPropertyName,这个时候先从 decryptedSystemEnvironment 开始找,经过 DefaultPropertyMapper 转换之后拿到的属性名称是 test.container-name,配置里面没有这个配置;然后从 systemEnvironment 开始找,经过 SystemEnvironmentPropertyMapper 转换之后拿到的属性名称是TEST_CONTAINERNAME 和 TEST_CONTAINER_NAME,根据 TEST_CONTAINER_NAME 就拿到了 ENC_VG9tY2F0 。这就解释了为啥配置类注入的还是加密之后的值了。
问题解决
知道问题的原理了之后,问题就好解决了。一种方法是可以在 DecryptEnvironmentPostProcessor 类的 postProcessBeforeInitialization() 方法中把添加的 MapPropertySource 类型改为 SystemEnvironmentPropertySource 就可以了。代码如下:- @Override
- public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
- String systemEnvName = StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
- MapPropertySource systemEnvSource = (MapPropertySource) environment.getPropertySources().get(systemEnvName);
- Map<String, Object> decryptedMap = new HashMap<>();
- if (systemEnvSource == null) {
- return;
- }
- systemEnvSource.getSource().forEach((key, value) -> {
- if (value instanceof String strVal) {
- if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(strVal) && strVal.startsWith("ENC_")) {
- String plainText = new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode(strVal.substring(4)));
- decryptedMap.put(key, plainText);
- }
- }
- });
-
- if (!decryptedMap.isEmpty()) {
- // 这里原来添加的是MapPropertySource类型,现在调整为SystemEnvironmentPropertySource类型
- // MapPropertySource decryptedSource = new MapPropertySource(DECRYPTED_SOURCE_NAME, decryptedMap);
- environment.getPropertySources().addBefore(systemEnvName, new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(DECRYPTED_SOURCE_NAME, decryptedMap));
- System.out.println("");
- }
- }
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作! |