1:
sql语句对大小写不敏感;
以分号结束 ;
2:
--单行注释:
'#' 单行注释:(可以后面不加空格,但推荐加上)
/* 多行注释 */
3 : DDL 数据库的定义
show databases;
use 数据库的名称
create database 数据库的名称 [charset utf8]
drop database 数据库的名称
select database(); 查看当前数据库
4: 表
show tables;
use helloworld ;
drop table student(表名称);
create table 表名称(
列名称 列类型,
列名称 列类型
);
int flaoat varchar() date timestamp
:5: 数据的插入,删除,更新
insert into 表名称(列1,......)values(值1,值2,.....),()
delete from 表名称[where 条件判断]
update 表名称 set 列=值 【where 条件判断】
字符串要用‘’ 括起来
点击查看代码- USE helloworld;
- delete from wcnm where name=3;
- delete from wcnm;
- insert into wcnm values(2,'woman');
- update wcnm set name=114514 where name=1;
- update wcnm set hex='一样的';
select 字段列表 | * from 表 [where ]
点击查看代码- select name,hex from wcnm;
- select * from wcnm;
- select * from wcnm where name=114514;
select hex,sum(name),avg(name),min(name),max(name),count(hex),count(*) from wcnm group by hex;
注意: group by 将表中数据按照指定列的值进行分组,把具有相同值的行归为一组
有去重的效果
8:结果的排序
limit : 限制几条的数据
SELECT → FROM → WHERE → GROUP BY → HAVING → ORDER BY → LIMIT
点击查看代码- select * from wcnm where name=2 order by hex asc; # 默让是asc升序
- # order by 排序 desc 降序 esc 升序
- select * from wcnm where name=2 limit 1;# 限制几条的数据
- select * from wcnm where name=2 limit 10,5; #跳过前面的10跳来展示后面的5条
- use helloworld;
- select namen,cout(*) from wcnm where name>50 group by name order by name limit 20;
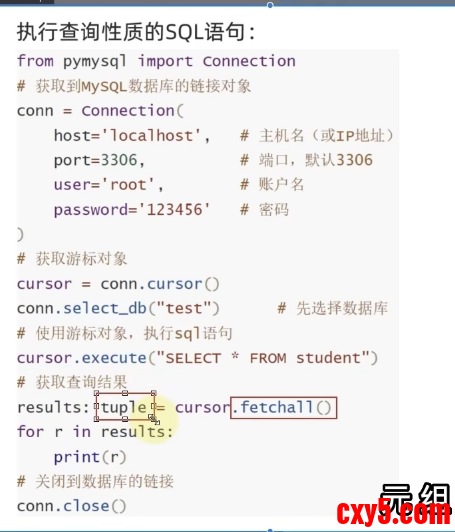
查询- # 从 pymysql 库中导入 Connection 类(这个类是创建数据库连接的核心模板)
- from pymysql import Connection
- # 构建 SQL 连接:通过 Connection 类创建实例 conn(即数据库连接对象)
- conn = Connection(
- host='localhost', # 数据库服务器的主机名/IP,localhost 代表本机
- port=3306, # MySQL 服务的端口号,默认是 3306
- user='root', # 连接数据库的用户名(root 是 MySQL 超级管理员账户)
- password='123456' # 连接数据库的密码(需替换为你自己的 MySQL 密码)
- )
- # 获取并打印 MySQL 服务器的版本信息(用于验证连接是否成功,返回如 8.0.32 这类版本号)
- print(conn.get_server_info())
- # ------------------------------ 执行 SQL 语句的核心逻辑 ------------------------------
- # 1. 获取游标对象:游标(cursor)是执行 SQL 语句的“工具”,所有 SQL 都通过游标执行
- cursor = conn.cursor()
- # 2. 选择要操作的数据库:指定后续 SQL 语句执行的目标数据库为 "helloworld"
- # 相当于在 MySQL 客户端执行 "USE helloworld;"
- conn.select_db("helloworld")
- # 【可选】执行非查询类 SQL(增/删/改/建表等),此处注释掉了建表语句
- # cursor.execute("create table text_plmysql(id int);")
- print("------------------------------")
- # 3. 执行查询类 SQL 语句:执行 "select * from wcnm",查询 wcnm 表的所有数据
- # execute 方法接收 SQL 字符串作为参数,负责把 SQL 发送给数据库执行
- cursor.execute(" select * from wcnm")
- # 4. 获取查询结果:fetchall() 会获取游标执行查询后返回的所有数据,返回格式是 元组嵌套元组
- # 比如 ((1, '王磊'), (2, '李娜'), ...),每一个内层元组对应表中的一行数据
- results = cursor.fetchall()
- # 5. 打印查询结果:输出 wcnm 表的所有数据
- print(results)
- # 6. 关闭数据库连接:释放数据库的连接资源(必须执行,否则会占用连接池)
- # 关闭后 conn 和 cursor 都无法再使用
- conn.close()
- ```plaintext
- from pymysql import Connection
- # 构建 SQL 连接:通过 Connection 类创建实例 conn(即数据库连接对象)
- conn = Connection(
- host='localhost', # 数据库服务器的主机名/IP,localhost 代表本机
- port=3306, # MySQL 服务的端口号,默认是 3306
- user='root', # 连接数据库的用户名(root 是 MySQL 超级管理员账户)
- password='123456', # 连接数据库的密码(需替换为你自己的 MySQL 密码)
- autocommit=True # 可以不加 默认是commit自己提交
- )
- # 获取并打印 MySQL 服务器的版本信息(用于验证连接是否成功,返回如 8.0.45 这类版本号)
- print(conn.get_server_info())
- # ------------------------------ 执行 SQL 语句的核心逻辑 ------------------------------
- # 1. 获取游标对象:游标(cursor)是执行 SQL 语句的“工具”,所有 SQL 都通过游标执行
- cursor = conn.cursor()
- # 2. 选择要操作的数据库:指定后续 SQL 语句执行的目标数据库为 "helloworld"
- # 相当于在 MySQL 客户端执行 "USE helloworld;"
- conn.select_db("helloworld")
- #执行命令
- #cursor.execute("insert into wcnm values(101,'老牛')")
- cursor.execute("select * from wcnm")
- print(cursor.fetchall())
- #手动提交
- conn.commit()
- #关闭
- conn.close()
来源:程序园用户自行投稿发布,如果侵权,请联系站长删除
免责声明:如果侵犯了您的权益,请联系站长,我们会及时删除侵权内容,谢谢合作! |